Receptor Subtypes in Detail
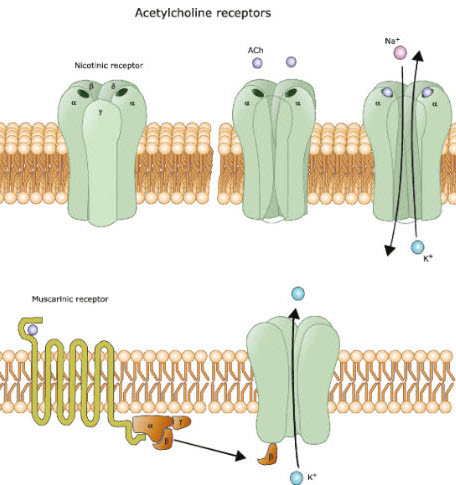
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Acetylcholine is a chemical that is found between the nerve synapses, or gaps, between nerve cells. When activated, it causes the contraction of skeletal muscles and activates glandular functions in the endocrine system.
- Travels through the Basal Forebrain to hippocampus, amygdala, & cerebral cortex
- Cholinergic receptors (nicotinic & muscarinic)
- Widespread loss of cholinergic neurons with Alzheimer’s Disease
- Anticholinergic response (dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention)
- Mechanisms also include learning & memory
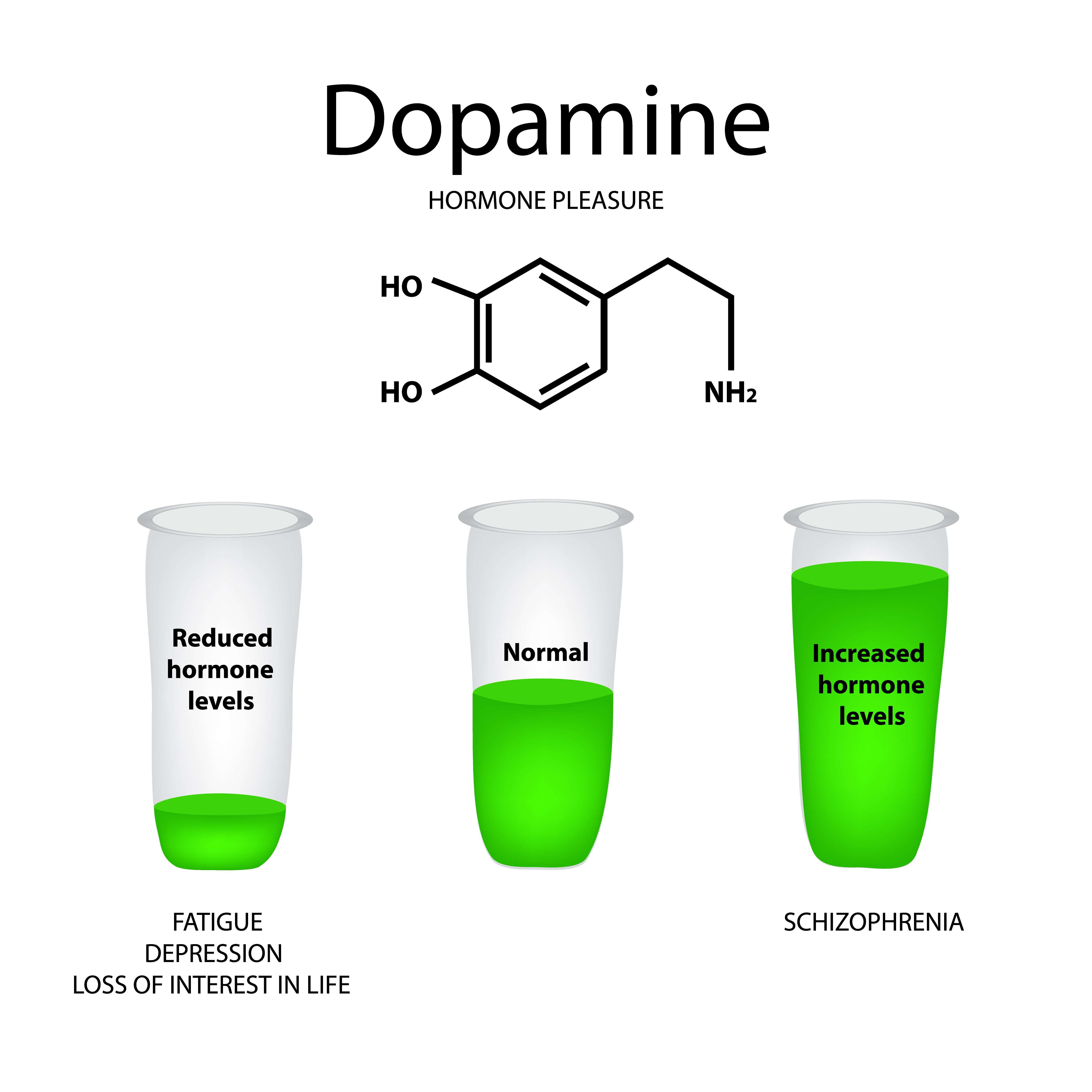
Dopamine
Dopamine is a chemical found naturally in the human body. It is a neurotransmitter that sends signals from the body to the brain.
Dopamine plays a part in controlling the movements a person makes, as well plays a role in how we feel pleasure. The right balance of dopamine is vital for both physical and mental wellbeing.
Located in cerebral cortex, limbic system.
Dopamine Hypothesis of Schizophrenia
- D2 over activity involved in psychosis
- All antipsychotics block D2
Cognitive Function = Attention, working memory, concentration
- Stimulants medications used for ADHD- enhance DA & NE via blocking reuptake or direct agonism
Parkinson’s Disease -Insufficient DA-agonists used to treat
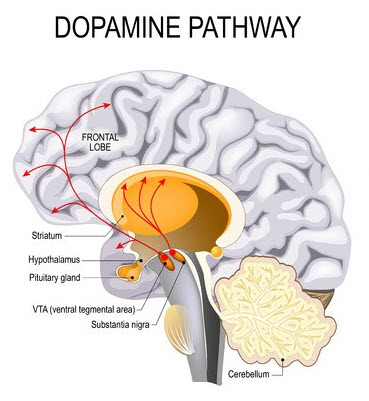
Dopamine Pathways
- Mesolimbic Pathway - Positive symptoms of Schizophrenia when DA is overactive (hallucinations, delusions)
- Nigrostriatal Pathway - Parkinsonism and other Extrapyramidal symptoms when DA is under active or depleted.
- Mesocortial Pathway - Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia; Cognitive problems
- Tuberoinfundibular Pathway - Elevated prolactin when DA is blocked (galactorrhea,gynecomastia, amenorrhea, impotence)
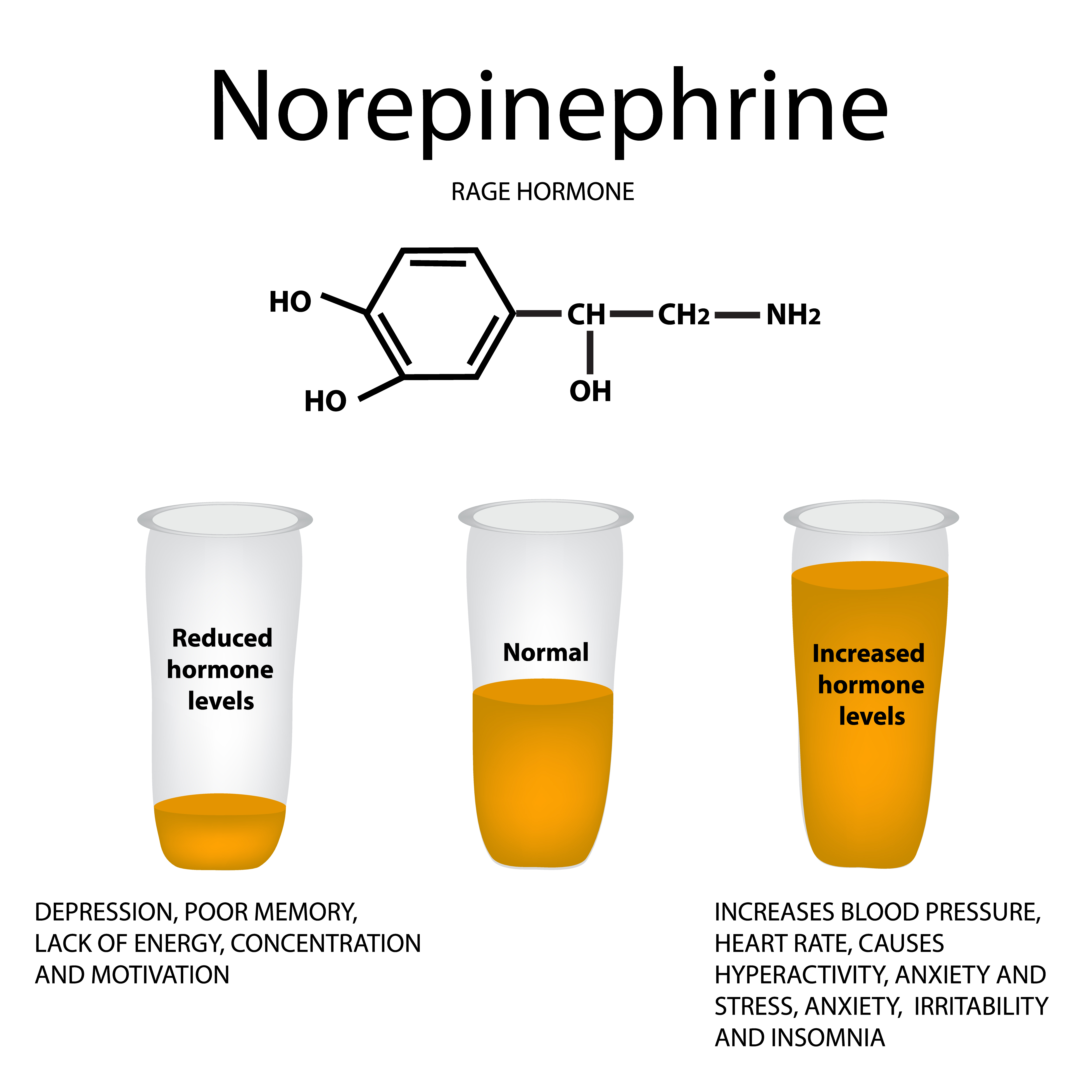
Norepinephrine (NE)
- Located in locus ceruleus in pons, cerebral cortex, limbic system, hypothalamus, & thalamus
- Receptors: Alpha1, Alpha 2; Beta 1; Beta 2
- Implicated in the following:
- Mood, arousal, sexual functioning
- Cognition
- Attention/Concentration
- Working Memory
- Information Processing
- Anxiety & Mood Disorders
- Psychomotor Activity
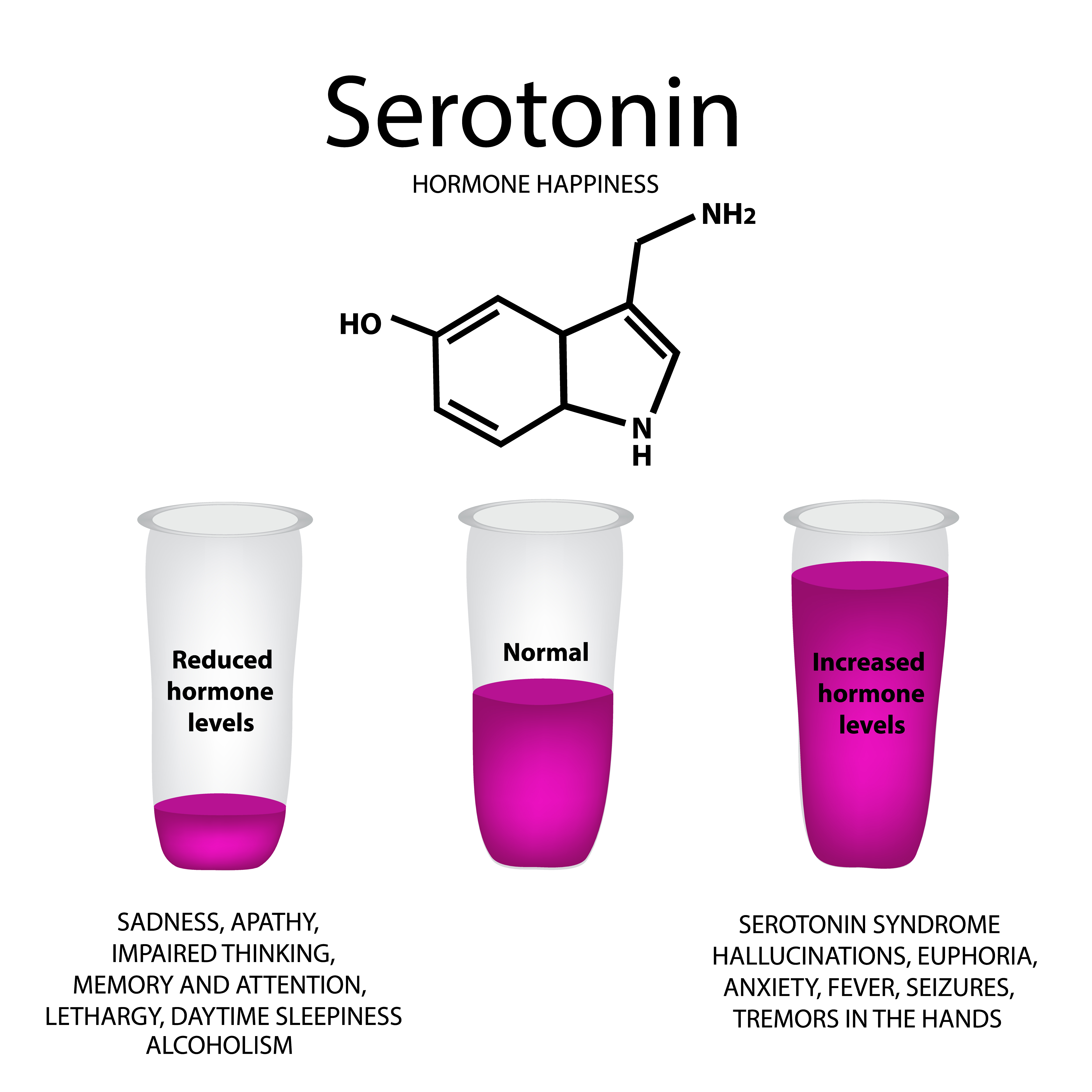
Serotonin (5HT)
- Located in raphe region of lower midbrain & upper pons; raphe nuclei, dorsal raphe, basal ganglia, & cerebral cortex
- Implicated in the following:
- Affective Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Impulsivity
- Aggression
- Obsessions & compulsions
- Food craving; bulimia
- Diurnal variation, sleep
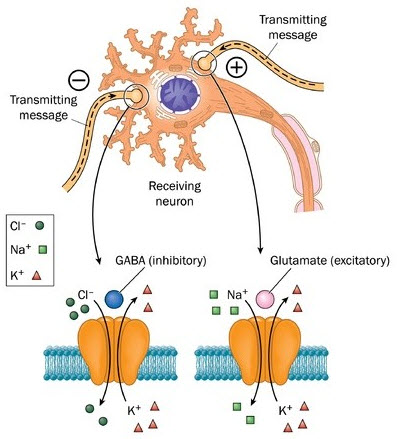
GABA and Glutamate = Amino Acids
Glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) are the major neurotransmitters in the brain. Inhibitory GABA and excitatory glutamate work together to control many processes, including the brain’s overall level of excitation. A balanced interaction is required to maintain the physiological homeostasis, while prolonged imbalance can lead to disease.
- Glutamate
- Major Excitatory NT in the brain
- GABA-gamma-aminobutyric acid
- Major Inhibitory NT in the brain
- GABA-A receptors are modulated by several nearby receptors
- Benzodiazepines
- Non-benzo sedative-hypnotics
- Alcohol
- Barbiturates