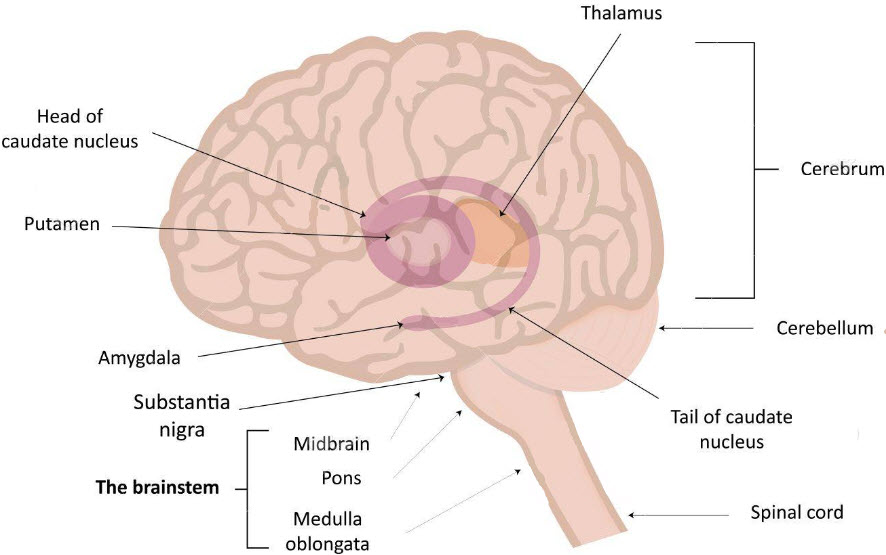
Basal Ganglia
The extrapyramidal system consists of a series of functionally related nuclei in the telencephalon, diencephalon and midbrain. The basal ganglia represent the largest component, and includes the caudate, putamen and globus pallidus.
- Subcortical group of gray matter nuclei
- Control system for muscle movements, motor control, and cognitive functions
- Mediates postural tone
- Part of the Extrapyramidal System
The basal ganglia are a group of structures found deep within the cerebral hemispheres. The structures generally included in the basal ganglia are the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus in the cerebrum, the substantia nigra in the midbrain, and the subthalamic nucleus in the diencephalon.
Function:
- Brings together emotion, exec function, motivation and motor activity.
- Involved in posture, motivation and motor activity.
- Controls extrapyramidal motor tract
Damage Effect:
- Slowness of movement, rigidity, cogwheel rigidity and dystonias.
Psychopathology:
- OCD
- Cognitive and emotional dysfunction
- Extrapyramidal tract symptoms
Damage to the basal ganglia cells may cause problems controlling speech, movement, and posture. This combination of symptoms is called parkinsonism. A person with basal ganglia dysfunction may have difficulty starting, stopping, or sustaining movement as seen in:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Huntington’s chorea
- Tourette’s