Limbic System
The limbic system is a set of brain structures that deal with emotions and memory. These structures regulate autonomic or endocrine function in response to emotional stimuli and also is involved in reinforcing behavior.
Made up of:
- Olfactory nerves, bulbs, & tracts - “nose brain”
- Amygdala
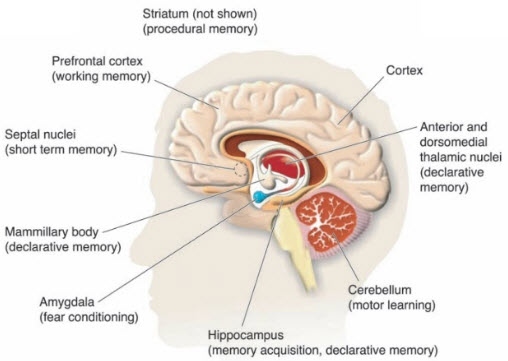
- Hippocampus
- Nucleus accumbens
- Hypothalamus
- Thalamus
Amygdala:
- Critically important gate through which internal and external stimuli are integrated. Damage to the amygdala has been reported to destroy the ability to distinguish fear and anger in other person’s voices and facial expressions.
Function:
- Anxiety and anger; generates rudimentary emotions like rage, religious ecstasy, sexual desire
- Contributes to establishing emotional memories
Damage Effect:
- Tumors assoc w/irritabiity, anger, rage and aggression
Psychopathology:
- PTSD, phobias, panic, depression, schiz, autism
Hippocampus:
- Important for making new memories—may be implicated in Alzheimer's Disease
- May be involved in depression and bipolar—appears to shrink
Function:
- Learning, memory, retrieval of information
- Builds cognitive maps; assigns time and place for the event
Damage Effect:
- Impaired ability to pay attention, learn new things, and remember or alter pre-existing learning
Psychopathology:
- PTSD
- volume in those w/depression, low self-esteem
Functions of the Limbic System:
- Emotional Memory
- Aggression
- Emotion
- Motivation-basic drives
- Appetite/eating
- Sex drive/activity
- Integration of smell