Principles Structures
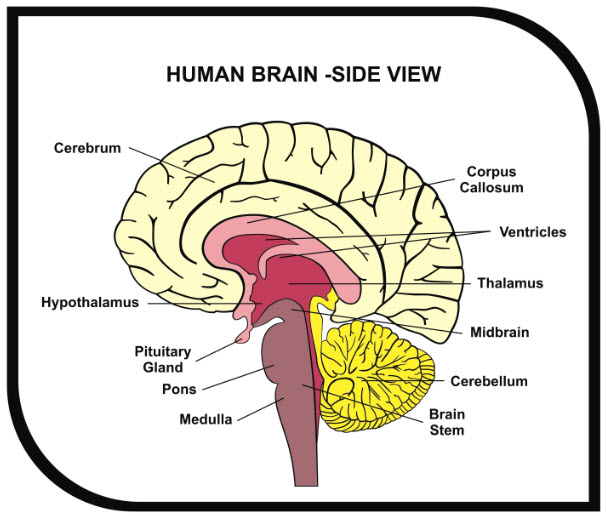
The brain contains various structures that have a multitude of functions. Listed here is a partial list of the structures.
Cerebral Cortex: Outer portion (1.5mm to 5mm) of the cerebrum that receives and processes sensory information
Basal Ganglia: Involved in cognition and voluntary movement
Limbic System Structures:
- Amygdala - involved in emotional responses, hormonal secretions, and memory
- Hippocampus - sends memories out to the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieves them when necessary
- Hypothalamus - directs a multitude of important functions such as body temperature, hunger, and homeostasis
- Olfactory Cortex - receives sensory information from the olfactory bulb and is involved in the identification of odors
- Thalamus - mass of gray matter cells that relay sensory signals to and from the spinal cord and the cerebrum
Tectum: The dorsal region of the mesencephalon (midbrain) that assists in visual and auditory reflexes
Tegmentum: The ventral region of the mesencephalon (midbrain) and includes the reticular formation and the red nucleus
Cerebellum: Controls movement coordination and maintains balance and equilibrium
Pons: Relays sensory information between the cerebrum and cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata: Lower part of the brainstem that helps to control autonomic functions