Labor (L)
ex. The number of nurses used to perform vaccinations.
|
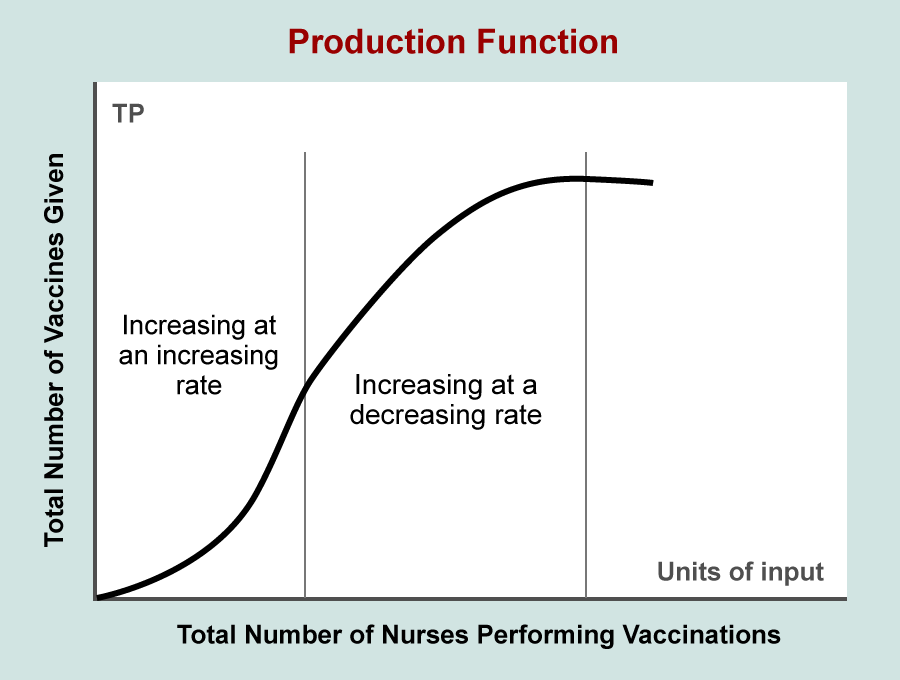
Number of Nurses (L) |
Vaccinations (Q or TP) |
Marginal Production of Labor |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0 |
----- |
|
1 |
20 |
20 |
|
2 |
45 |
25 |
|
3 |
65 |
20 |
|
4 |
80 |
15 |
|
5 |
90 |
10 |
|
6 |
95 |
5 |